When it comes to software or firmware, the starting point for coding usually begins with understanding 'Hello World,' and getting to know Nuvoton's MCU is no exception. Today, let's explore how Nuvoton's MCU gets started through this classic example.
The sample code for this template is very simple. It uses the UART TX and RX on the ICE to display a string of 'Hello World' on the computer terminal.
Example code:https://github.com/OpenNuvoton/M031BSP/blob/master/SampleCode/Template/main.c
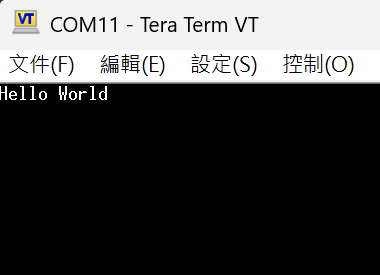
There is one thing to note here: there is a toggle switch on the development board. You need to first enable TXD and RXD so that the UART functionality can be transmitted to the computer terminal via ICE through USB. Please set the computer terminal to 115200 8N1, and you should be able to see the information smoothly.
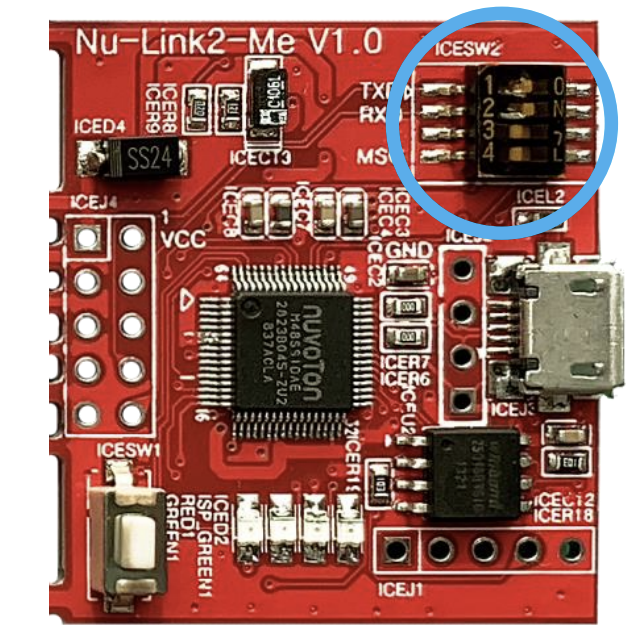

If the pins are already insufficient and there's no way to pull out an extra UART for message printing, what can be done? Here's another little trick: you can use Semihosting. This way, you can still see relevant messages during debugging. Let's dive into the process together!
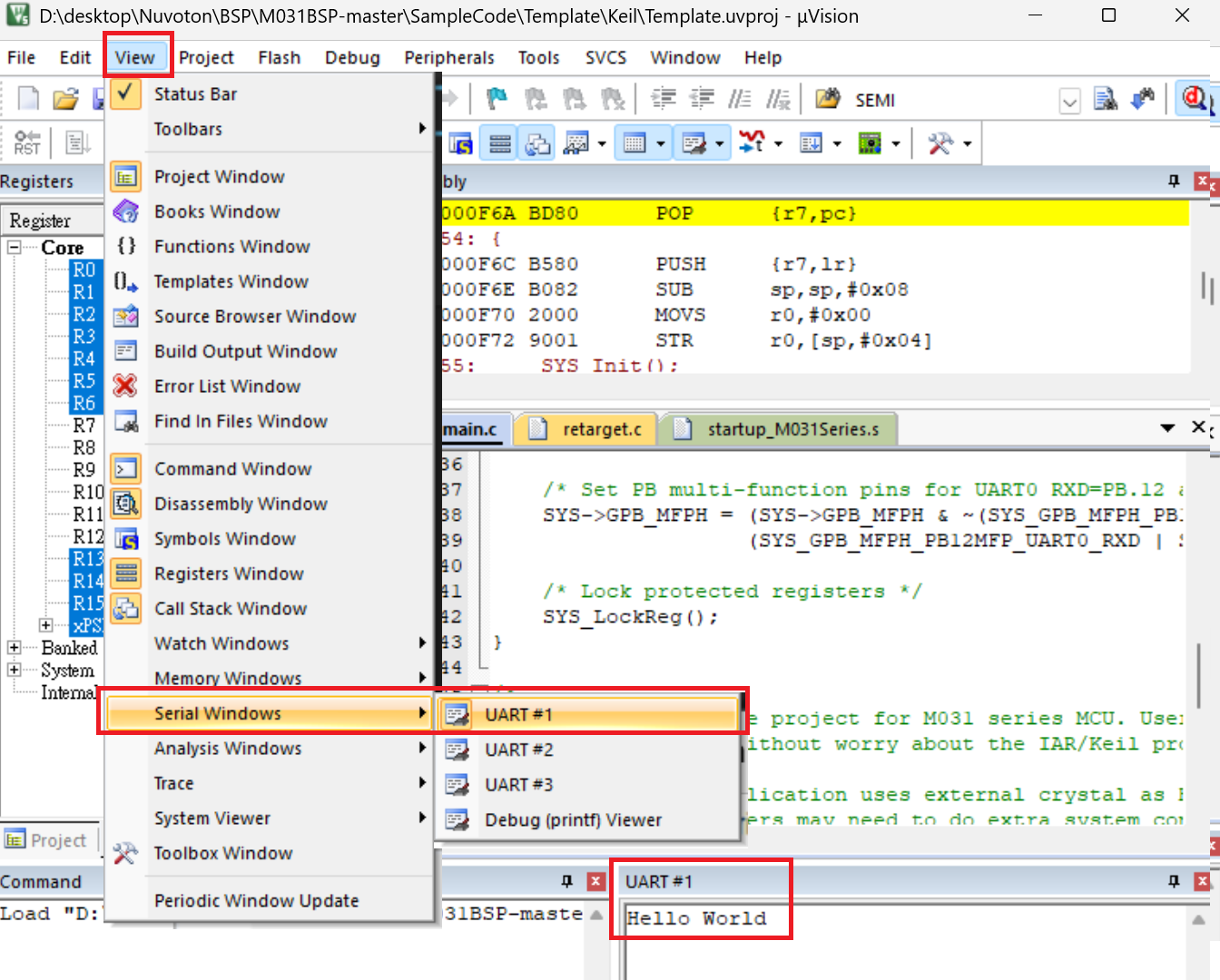
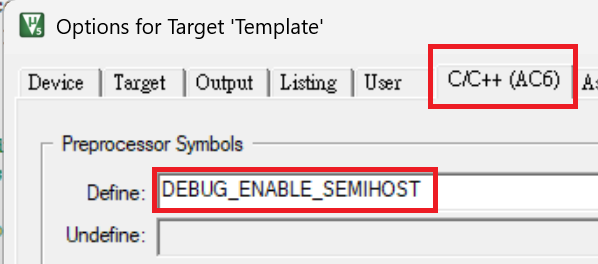
First, define DEBUG_ENABLE_SEMIHOST under Options for Target -> C/C++, then compile and reflash the program.
After entering Debug mode, go to View -> Serial Windows -> UART #1, then continue executing the program. You will see the printed strings in the UART #1 window.