1.概述
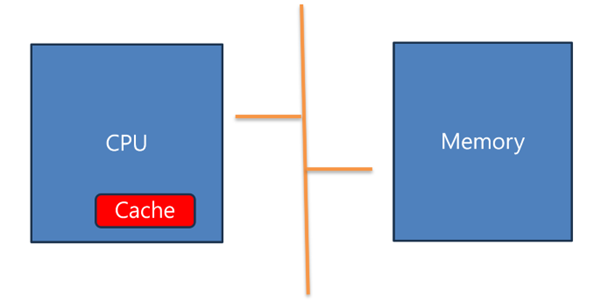
微控制器是一種集成電路,通常由一個或多個中央處理單元(CPU)、內存、輸入/輸出及其他支持功能組成,內存分為非易失和易失性存儲器;微控制器上電先從非易失存儲器將可執行程序搬運易失性存儲器,然後開始運行;程序運行過程中 CPU 需要不斷地從內存(或其他存儲器)讀取指令和數據,CPU 需要等待指令或數據讀取完成,才能進行數據處理,即便 CPU 的速度再快,最後程序運行速度受限於內存(或其他存儲器);如果將內存更換為處理速度更快的內存,則會大大增加微控制器的成本;為解決上述問題,微控制器內核引入 Cache 技術,Cache是一段高速的、size 較小的 RAM,Cache 的讀、寫速度要比內存(或其他存儲器)快,作為 CPU 與內存(或其他存儲器)之間的橋樑。
2. Cache 分類
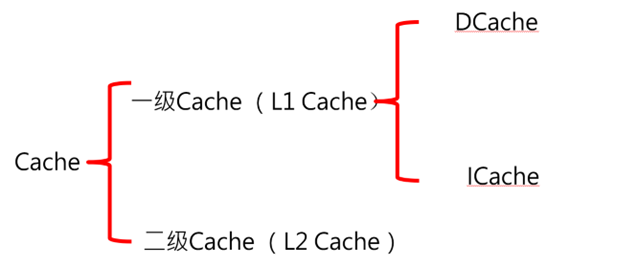
Cache 分為一級 Cache 和 二級 Cache,本書僅介紹一級 Cache,一級 Cache 又分為 I-Cache 和 D-Cache,大小一般為 32KB,比如 Cortex-R5 內核,I-Cache 用於存儲指令而 D-cache 用於存儲數據,I-Cache 與 D-Cache 可以獨立的打開和關閉,由於 I-Cache 用於緩存代碼本文不予討論,D-Cache 用於存儲數據,D-Cache 使用不當會導致一些隱患,本文只講解 D-Cache 的使用,且默許 I-Cache 為打開狀。
3. Cache 專業術語
命中:CPU 要訪問的數據在 Cache 中有緩存;
缺失:CPU 要訪問的數據不在 Cache 中,CPU 需要去內存(或其他存儲器)讀取數據;
Cache size:Cache 可以緩存最大數據的大小;
Cache line:CPU 讀取或寫入內存(或其他存儲器)最小傳輸字節;
Dirty bit:每一行 Cache line 只有一個 Dirty bit,當 Dirty 位有效時,Cache Line 中的數據不能隨意丟失,需要寫回內存(或其他存儲器);
Valid bit:這個 bit 用來表示 Cache line 中數據是否有效,若被尋址數據在Cache 中命中,但是 Valid bit 無效,也是 Cache 缺失;
Offse、Index:概念見下一章節;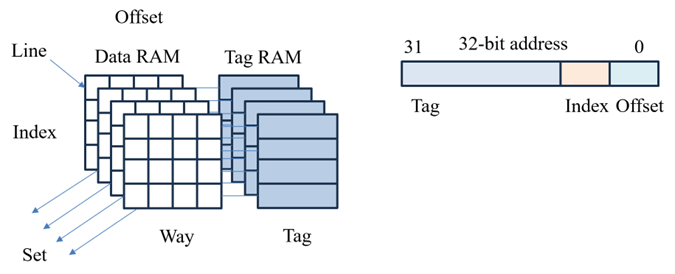
4. Cache 基本原理
Cache是一段高速的、size 較小的 RAM,Cache 的讀、寫速度要比片內或片外內存快,作為 CPU 與內存(或其他存儲器)之間的橋樑;當 CPU 訪問數據時,根據被訪問數據的地址,確定數據是否在 Cache 中緩存,若在 Cache 中緩存,則命中可直接使用數據,若不在 Cache 中緩存,則需要去內存(或其他存儲器)讀取。強調一下 Cache 屬於內核的一部分,若在多核系統中,多核訪問同一片地址的數據,會引起什麼問題,如果啟動 DMA 技術,同時打開 Cache,會引起什麼問題?
直接映射緩存:假設 Cache Size 為 64 byte,Cache Line 為 8 byte,平均為分 8 行;Cache Line 為 8 byte,需要用 3 bit 尋址 Cache Line 中的某一個字節,所以 Offset 需要 3 bit;Cache 總共分為 8 行,需要用 3 bit 尋址 8 行中的某一行,所以 Index 需要 3 bit,其他地址位存放到 Tag 中,直接映射緩存由於可能會引起 Cache 顛簸,接下來引入多路組相連緩存概念;
假設尋址 RAM 地址為 0x0654(0110 0101 0100),數值為 0x12,其中 Offset 為 4,Index 為 2,Tag 為 19。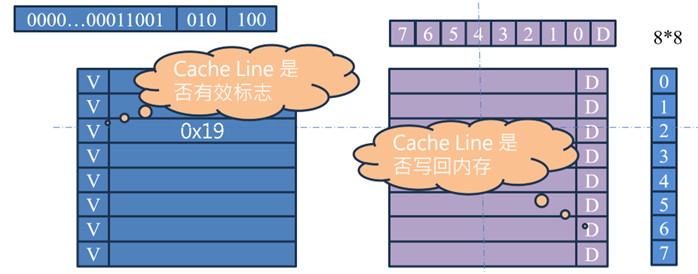
兩路組相連緩存:假設 Cache Size 為 64 byte,平均分為 2 份,每一份為 32 byte,由於 Cache Line 為 8 byte,每一路組為 4 行 Cache Line,其中需要用 2 bit 尋址一組中某一行,所以 Index 需要 2 bit, Cache Line 為 8 byte,需要用 3 bit Cache Line 中的某一個字節,所以 Offset 需要 3 bit,其他地址位存放到 Tag ,當尋址的地址中 Offset、Index 都匹配時,不能準確定位被尋址地址在某一路組,需要將 Tag 數據與被尋址數據再次比較,才能準確定位數據空間,由於此方式增加了比較次數,所以對硬體要求比較高。
假設尋址 RAM 地址為 0x0654(0110 0101 0100),數值為 0x12,其中 Offset 為 4,Index 為 2,Tag 為 0x32。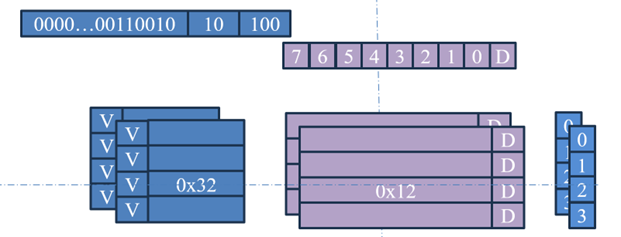
5. Cache 分配策略
- 寫通(write through),CPU 向內存中寫數據,首先檢查 Cache 中是否有數據備份,如果有則寫入到 Cache,之後立即再次寫入到內存。
- 寫回(write back),CPU 向內存中寫數據,首先檢查 Cache 中是否有數據備份,如果有則將數據寫入到 Cache, 之後並不會立即將數據寫入到內存,等待空閒時自動將數據更新到內存。
- 寫分配(write alloc),CPU 向內存中寫數據時,首先檢查 Cache 中是否有備份,如果沒有則將會在 Cache 中分配空間,備份寫入到內存的數據。
- 讀分配(read alloc),與寫分配類似,CPU 讀內存時首先檢查 Cache 中是否有備份,如果沒有則在 Cache 中分配空間,備份將要讀取的數據。默認情況下讀分配是開啟的。
- Cache 清理,Cache 清理並不是刪除 Cache 中的內容,而是將 Cache 中的內容更新到各自對應的內存中。
- 緩存無效化,Cache 中的內容失效,效果如同刪除了 Cache 中的數據備份,CPU 再次讀數據時將直接從內存中讀取。
- 多個核心使用同一個變量,一個核心寫變量後變量值還在 Cache 中而沒進入 IRAM 中(可以通過設置屬性 Write-through 解決),導致另一個核心看不到。
- 一個變量的值被 Cache 到某個核心的 Cache 中,如果 IRAM 中的值改變了,此核心直接嘗試讀此值讀到的依然是 Cache 中的舊值。
- 由於 Cache line 是 32 字節,維護 Cache 的最小單位也就是 32 字節,如果一個變量小於 32 字節,當某個核心在維護 Cache 時,可能會導致在此 Cache line 中其它數據也受到影響。因此建議各個 core 的私有數據段(如該數據段 Cacheable)Cache line 對齊,從而避免一個 core 發生 Cache 替換或 Cache 維護時影響另一個 core 數據的情形。
- 在使用一些加速器時,如 DMA 等,需要對 DMA 操作的區域做 Cache 維護操作。
- Cache enable
/**
* @brief Enable ARM I-Cache and D-Cache operations.
*
* If CONFIG_ARCH_WITH_CACHE is defined, ARM I-Cache and D-Cache
* operations are enabled and you can call functions defiend in cache.h to
* manage caches.
*/
#define CONFIG_ARCH_WITH_CACHE 1
/**
* @brief ARM cache line size in bytes.
*
* Cortex R5 cache line length is 8 words (256 bits).
*/
#define CONFIG_ARCH_CACHE_LINE 32
/**
* @brief Enable I-Cache on power up.
*
* If CONFIG_ARCH_EARLY_ENABLE_ICACHE is defined, ARM I-Cache is
* enabled on power up.
*/
#define CONFIG_ARCH_EARLY_ENABLE_ICACHE 1
/**
* @brief Enable D-Cache on power up.
*
* If CONFIG_ARCH_EARLY_ENABLE_DCACHE is defined, ARM D-Cache is enabled on
* power up.
*/
#define CONFIG_ARCH_EARLY_ENABLE_DCACHE 1
- Cache API
/*
* enable caches.
* @flags cache type.
*/
void arch_enable_cache(uint8_t flags);
/*
* disable caches.
* @flags cache type.
*/
void arch_disable_cache(uint8_t flags);
/*
* clean dcache.
* @start start address.
* @len clean data length.
*/
void arch_clean_cache_range(addr_t start, size_t len);
/*
* clean and invalidate dcache.
* @start start address.
* @len clean data length.
*/
void arch_clean_invalidate_cache_range(addr_t start, size_t len);
/*
* clean and invalidate dcache all
*/
void arch_clean_invalidate_dcache_all(void);
/*
* invalidate dcache.
* @start start address.
* @len clean data length.
*/
#define arch_invalidate_cache_range(start, len)
/*
* sync dcache.
* @start start address.
* @len clean data length.
*/
void arch_sync_cache_range(addr_t start, size_t len);
7.2 MCAL Cache
- Cache enable
arch_enable_cache(ICACHE | DCACHE);
- Cache API
void arch_disable_cache(uint32 flags);
void arch_enable_cache(uint32 flags);
void arch_sync_cache_range(unsigned long start, uint32 len); //invalidate icache
void arch_clean_cache_range(const void *start, uint32 len);
void arch_clean_invalidate_cache_range(const void *start, uint32 len);
void arch_invalidate_cache_range(const void *start, uint32 len);
void arch_set_dcache_error_check(void);
8. 參考文檔
《AppNote_E3_Boot_and_OTA_Rev01.06》
《E3400_E3600_MCU_TRM_Rev00.13》
歡迎在博文下方留言評論,我們會及時回復您的問題。
如有更多需求,歡迎聯繫大聯大世平集團 ATU 部門:atu.sh@wpi-group.com 作者:娜就這麼嘀
更多資訊,請掃碼關注我們! 
評論